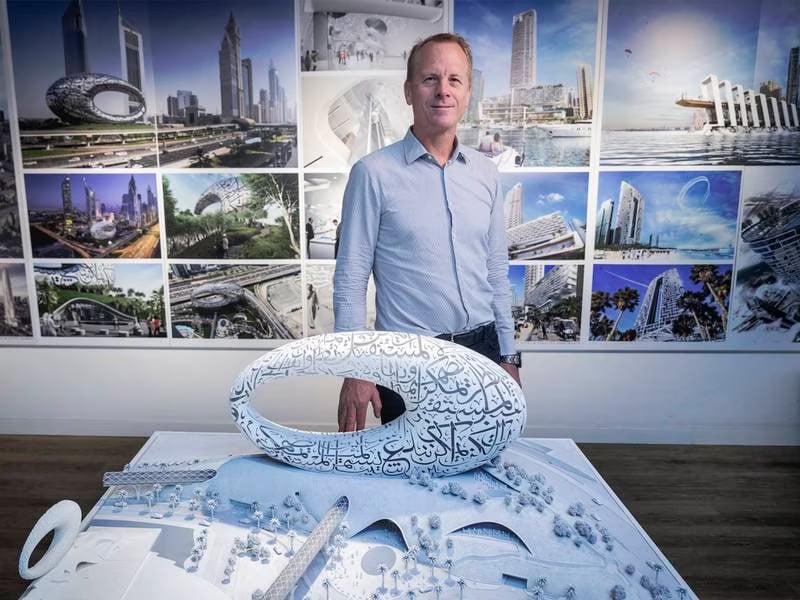
Shaun Killa: the architect who dreamt up the design of Dubai’s Museum of the Future.

With only three weeks to go, Shaun Killa cast aside the sketches piled on his dining-room table. The South African architect was aiming to win a fierce international six-week design competition for a new building in Dubai.
It was an unusual brief and Killa knew the sketches needed more.
“I just felt they weren’t good enough,” Killa says of the designs. “Not good enough to win.”
As the clock ticked past midnight, he continued to sketch, using only tracing paper and a pen.
“I really searched deep,” he says. In the end, it took only a few minutes. Hand-drawn at 1am on his dining table, the design became a building that has energised and reshaped Dubai’s skyline.
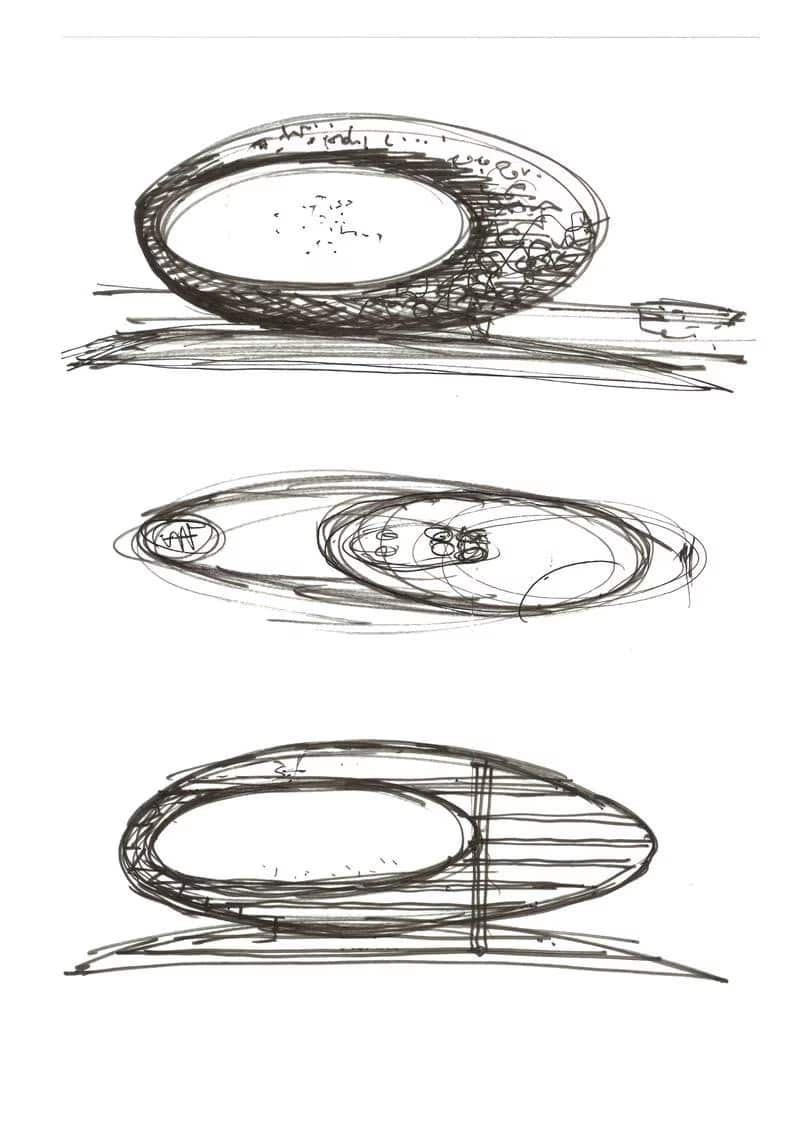
“I love buildings with shapes that feel that they move,” he says, pointing to the original sketch he drew in the early hours of the morning, which now hangs on the wall.
“The building looks like it wants to move down the Sheikh Zayed Road. And look at the calligraphy. It was there from the start.”
Killa then used WhatsApp to send a photograph of the sketch to a colleague who was doing the computer modelling. “The next morning he wrote back, “I don’t understand’,” Killa says with a smile.
A new symbol of the future
More than six months since the Museum of the Future’s opening, the star architect is reflecting on his achievement at his offices in Dubai. He established Killa Design in 2015, and from the windows one can see Dubai World Trade Centre. This was once a building that represented the future, but now Killa’s design for Museum of the Future has taken the baton on the road to tomorrow.
For a story about the future, it begins in the past at a time when Dubai was going through one of the most transformative periods in its young history. Killa moved to the city from Cape Town in the 1990s after a friend said “interesting things” were happening. None more so than Burj Al Arab, a glitzy new hotel rising on a man-made island off the coast.
“I also saw Emirates Towers under construction,” Killa says. “There was an energy in the city. There was an optimism.”
He joined the Atkins design firm in 1998 to work on the Burj, only a year before the famous hotel opened. It was totally different from anything he had done in South Africa.
“The Burj increased my perspective,” he says. “It is that change of scale and out-of-the-box thinking. But I also had my own drive.”
That drive led him to become director of architecture with Atkins and a succession of projects followed that redefined architecture in the UAE and Middle East, such as the renowned Bahrain World Trade Centre that used wind turbines to generate some of the building’s electricity. Killa was also behind Dubai Opera in 2016 and the curves of the building provide a signpost to his designs of today.
But Killa wanted to forge his own path and left Atkins. In 2015, shortly before he founded Killa Design, Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid, Vice President and Ruler of Dubai, announced a Museum of the Future was to be built and Dubai Future Foundation was handed responsibility for the project. One requirement was that it needed to sit somewhere on the site of Emirates Towers.
Crucially, Killa in his proposal decided against using a site at the rear of Emirates Towers and instead, pinpointed a small space beside Sheikh Zayed Road that at the time was a car park surrounded by trees as having the most potential.
“If I put the museum behind Emirates Towers, 2 per cent of the people would know it’s there,” he says. “But if I put it on Sheikh Zayed Road, then 100 per cent of people will know it’s there. And I can connect Dubai Metro to the museum and the museum to Emirates Towers.”
Because the space was quite small, Killa knew the building needed to be vertical. He describes early designs as organic, which means they were all flowing lines and shapes. Killa, an admirer of abstract art, explains how the oval and the void ― the hole through the middle ― were drawn at the same time.

“Throughout my career, I haven’t been afraid of shapes which are progressive,” Killa says.
Pointing to the sketch of the void, he says this presses the oval to one side to elongate the building and hand it a sense of dynamism. “Otherwise it would feel still,” he says. “It has a sense of speed. It has a sense of direction as opposed to a sphere. It also is very natural. But what I like about it is this sense of direction.”
The void, Killa says, represents what we don’t know about the future. It was envisaged as a place where the museum could stage visual displays, but its role goes beyond practicality.
“This is the most powerful point of the whole building,” he says. “People who seek the unknown are the people throughout the ages who have discovered new things and invented new things. That will replenish the museum and keep it abreast of time.”
Killa was invited to present his designs for Museum of the Future at the prime minister’s office before he realised he had won. Afterwards he was informed he must start the very next day. “Come back here tomorrow morning,” Killa recalls the instruction with a smile.
A ‘complex and delicate’ process
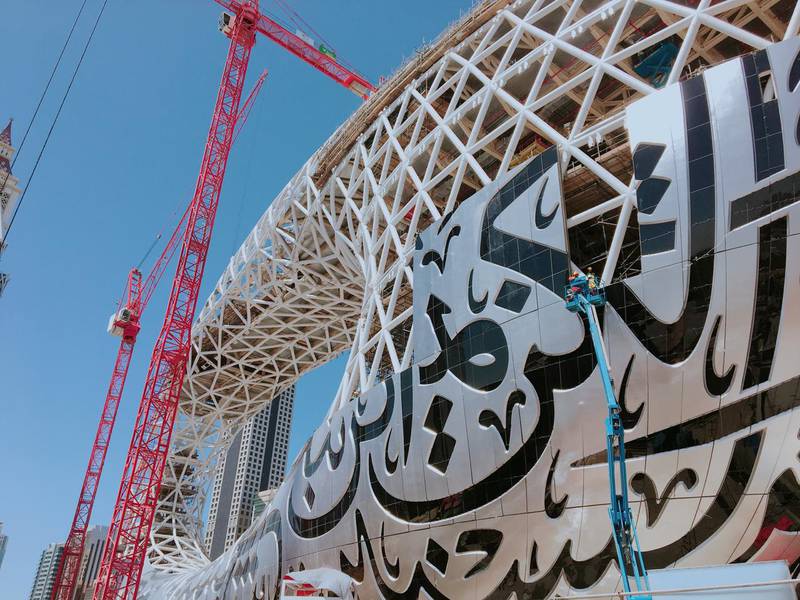
Museum of the Future is 77 metres tall and covers an area of 30,548 square metres. It has seven storeys of exhibition space, a 420-seat auditorium, restaurant, cafe and lobby. The oval shape aims to represent humanity; the green mound it sits on top of represents the Earth; and the void represents the unknown future.
The engineering process ― completed by Buro Happold ― was complex and delicate. Museum of the Future does not have traditional support columns but instead is a steel diagrid ― a frame of beams ― and was developed with the aid of algorithms and a software system known as Building Information Modelling. The facade is just as complex. It consists of 1,024 pieces and was designed using techniques from the aviation industry in how they applied it like a skin on to the building.
Window designs, in the form of Arabic calligraphy by Emirati artist Mattar bin Lahej and based on Sheikh Mohammed’s quotes, are also mapped on to this curved skin. The quotes also function as windows into the museum and are illuminated at night with LEDs. The double staircase in the lobby used bended steel so large that submarine contractors used to bending huge steel nose cones were called in to do it. Sustainability is also important and the building uses solar power.
“The building is like a baton that pays homage to Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid’s father, then his vision with his own words and [then] passing that on to his future generations. That’s what the building symbolises.”
The museum was named one of the 14 most beautiful museums on the planet in a list compiled by National Geographic magazine months before it opened. But it wasn’t until the scaffolding came down and people walked through its doors for the first time in February that Killa was able to really enjoy it.
“I walked into the reception, sat down and got a coffee,” he says of that first day. “No one knew who I was. I saw hundreds and hundreds of people in that lobby with kids, adults smiling and taking pictures and enjoying themselves.
“At that point, I realised the building is for the visitors and residents of Dubai and the UAE. We are creating experiences about … how the unbelievable can become the believable and how the impossible can become possible. It is almost a building of fantasy. Now it is owned by the people.”





